Explore the fascinating world of the vagus nerve, affectionately dubbed the “wanderer,” as it meanders through your body, orchestrating a symphony of healing. This article delves into the wondrous capabilities of the vagus nerve, traditionally known for its role in keeping your heart beating and your digestion humming. Yet, recent discoveries reveal its superpower: a knack for soothing inflammation, boosting immunity, and even uplifting your mood. Join us on this exploration as we uncover the secrets of this extraordinary nerve and its potential to transform your health and well-being.
Welcome to the world of the vagus nerve, where science meets wonder, and healing takes center stage. Long seen as a backstage player in the drama of bodily functions, this nerve is now stepping into the spotlight, revealing its profound influence on how we feel, think, and heal. Let’s embark on a journey to unveil the hidden powers of the vagus nerve and how they can enrich our lives with vitality and balance.
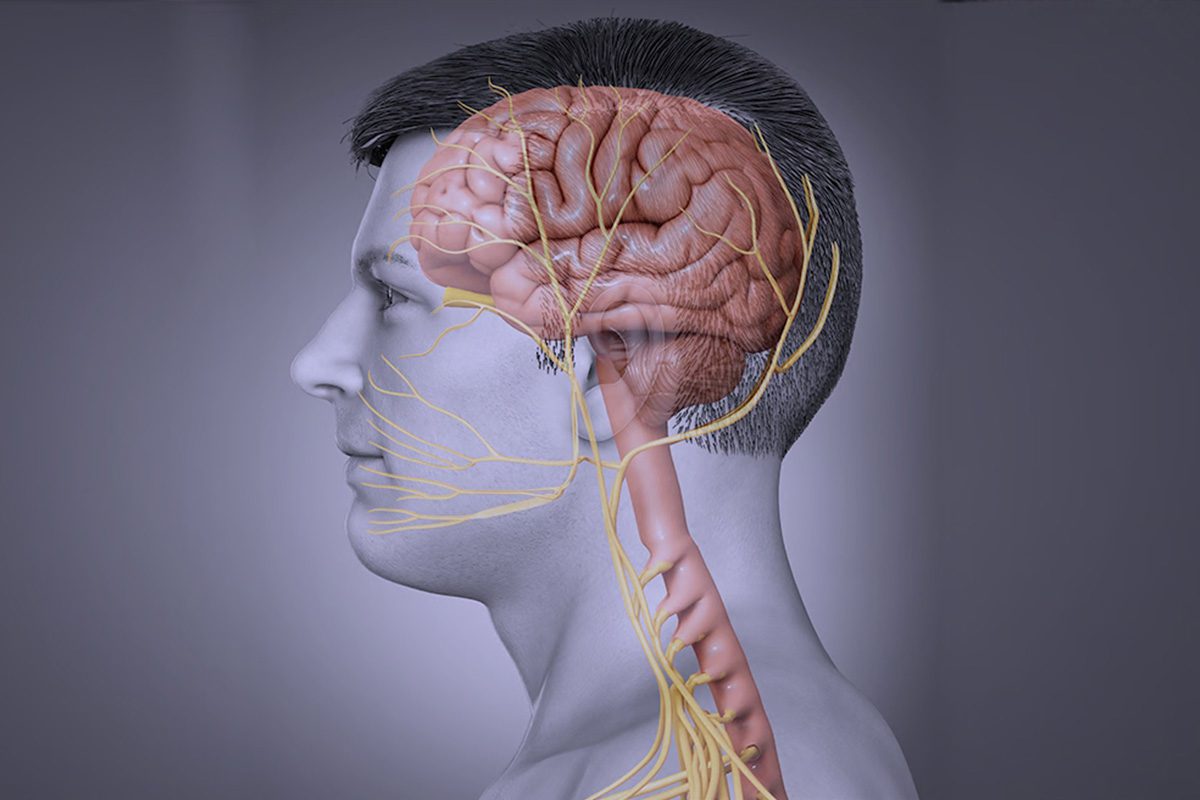
Anatomy of the Vagus Nerve:
Picture a delicate, branching highway stretching from your brainstem to every corner of your body, connecting your heart, gut, and more. That’s the vagus nerve, your body’s built-in communicator, ensuring seamless communication between your brain and vital organs. It’s like nature’s Wi-Fi network, keeping everything in sync for optimal health and well-being.
Physiological Functions of the Vagus Nerve:
Now, let’s dive into what the vagus nerve can do:
1. Heart Harmony:
Feel that sense of calm after a deep breath? Thank your vagus nerve, which helps slow down your heart rate, promoting relaxation and reducing stress.
- When you inhale deeply, your lungs expand, sending signals through the vagus nerve to your brain. In response, the brain activates the parasympathetic nervous system, which is like the body’s relaxation mode. The vagus nerve plays a crucial role in this process by sending signals to the heart to slow down its beating rate.
- As the heart rate decreases, your body shifts into a state of relaxation. This is accompanied by lower blood pressure, reduced muscle tension, and a sense of calmness washing over you. All of these physiological changes contribute to a feeling of overall relaxation and well-being.
- By slowing down the heart rate and promoting relaxation, the vagus nerve helps counteract the effects of stress on the body.
2. Gut Guardian:
The vagus nerve has anti-inflammatory powers that help quell the flames of inflammation, supporting your body’s healing process.
- When activated, the vagus nerve releases acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that binds to receptors on immune cells called macrophages. This binding inhibits the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. This mechanism is known as the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
- By dampening the inflammatory response, the vagus nerve helps maintain a balanced immune system and prevents excessive inflammation that can contribute to various health conditions, including chronic inflammatory disorders. This regulatory function of the vagus nerve is crucial for promoting healing and maintaining overall health and well-being.
Mood Manager:
Need a mood boost? The vagus nerve releases feel-good neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and serotonin.
- Acetylcholine is involved in various cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and learning. It also plays a role in regulating mood and emotional responses. By modulating activity in certain brain regions, acetylcholine helps promote feelings of relaxation, calmness, and contentment. Acetylcholine is also known to enhance communication between nerve cells in the brain, which may contribute to a sense of mental clarity and well-being.
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) is often referred to as a “stress hormone” because it is released in response to stressful situations. However, it also plays a key role in regulating mood and arousal. In moderate levels, norepinephrine helps promote alertness, focus, and motivation, which can contribute to a positive mood and sense of vitality. Norepinephrine is involved in the body’s “fight or flight” response, but it also influences mood regulation by affecting brain regions involved in emotional processing and mood stability.
- Serotonin is often called the “happiness neurotransmitter” because of its strong association with mood regulation and emotional well-being. Serotonin helps regulate mood by modulating the activity of neurons in the brain regions responsible for mood control, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
In Conclusion
the vagus nerve emerges as a remarkable orchestrator of healing and well-being, connecting mind and body in profound ways. From its foundational role in maintaining heart harmony and digestive balance to its anti-inflammatory and mood-regulating effects, the vagus nerve holds the key to unlocking the body’s innate healing potential. By understanding and harnessing the power of the vagus nerve, we can embark on a journey towards holistic wellness, cultivating resilience, vitality, and inner peace. In our next article, we will delve deeper into the transformative potential of yoga practices specifically designed to stimulate the vagus nerve, offering practical insights and techniques to enhance our connection to this vital pathway of healing and vitality. Join us as we explore the synergy between yoga and the vagus nerve, paving the way for a deeper understanding of mind-body integration and holistic health.